Chemical milling is a subtractive machining technique that involves removing material for the desired shape in baths of temperature-controlled etching chemicals. It is described as a technique for producing blind features like pockets, channels, etc., by chemically eroding the material. To reduce weight, it also eliminates material from every surface of the components. Dipping the workpiece in chemical reagents or etchants, such as acids and alkaline solutions, removes material from specific workpiece locations during chemical machining (CM).Read More…
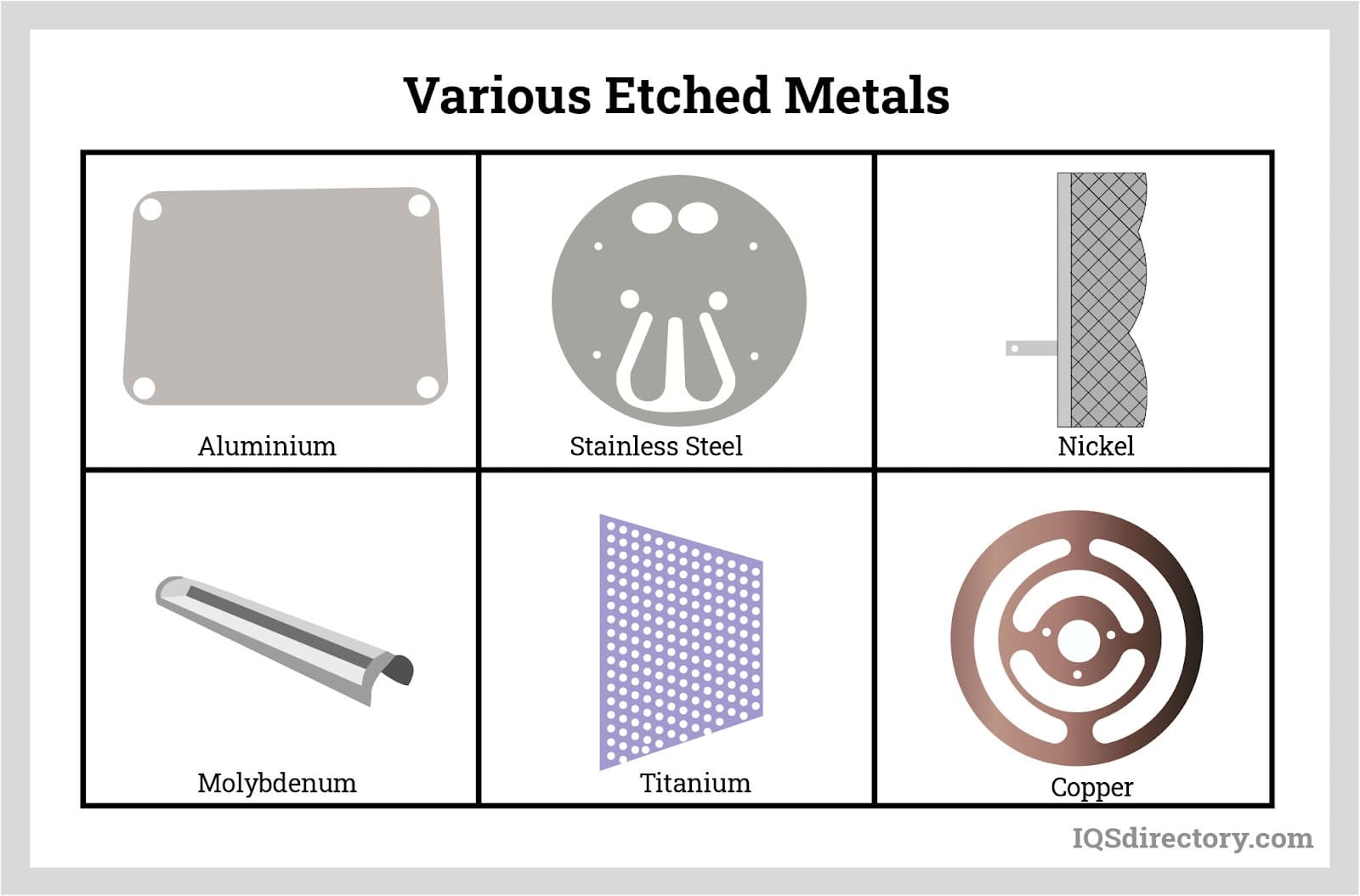
Great Lakes Engineering is a trend setting manufacturer of surface mount stencils, precision laser cut parts, and photo chemical etched parts. We work with a wide range of materials, including Stainless Steel, Copper, Titanium, Nitinol, Nickel, Kovar and many others.

VACCO is the industry leader of Photo Chemical Etching of metal & polyimide components and devices. We specialize in Stainless steel, Titanium, and Copper, but work with a variety of different materials. We have over 60 years of experience in Chem Etching, and we offer Micro Laser Cutting & Welding, and Diffusion & Adhesive Bonding services along with an extensive range of value-added services. ...

The MET Manufacturing Group, LLC process offers many technical & financial advantages in manufacturing various flat metal components. Try this precision etching, non-mechanical process for competitively priced, burr & stress free sheet metal products, up to 62 mil (.062”) thick. Our photo-chemical machining process is also known as photo-fabrication, photo etching, chemical milling & acid...
Etchit is your high-quality solution for custom-manufactured precision metal parts and components. We use photochemical machining to make products for such industries as aerospace, audio, automotive, computer, circuit board, decorative and fastener. Does your product need photo etching processes?

Photochemical machining is the process we use on aluminum (and alloys), brass, copper, inconels, kovar, metal foils (less than .001” thick), metal sheets (up to .125” thick), mild steels, molybdenum, monels, nickel, phosphor bronze, stainless (300 & 400) and others. Trust your metal etching needs to us.
More Chemical Milling Companies
When metals corrode or dissolve chemically, the material is eliminated via microscopic electrochemical cell action. Even though the penetration rates of the material removal may only be 0.0025–0.1 mm/min, this regulated chemical dissolution will concurrently etch all exposed surfaces. Although heavier metal objects like coins and plaques can be etched, etched metals are typically thin, like sheet metal or foil. If carried out by skilled personnel, chemical milling is a specialized procedure that can save manufacturers time and money.
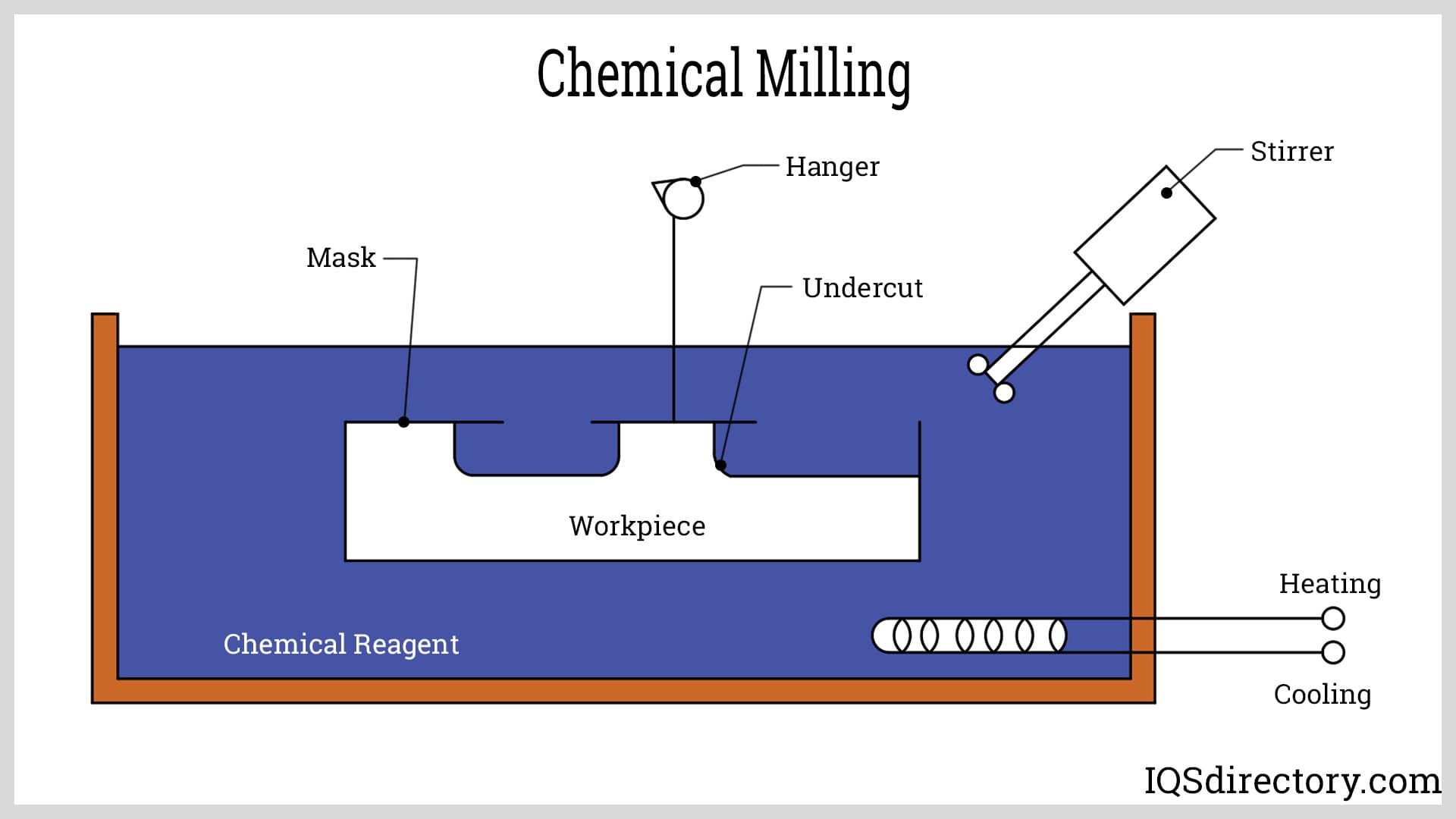
How Chemical Milling Works
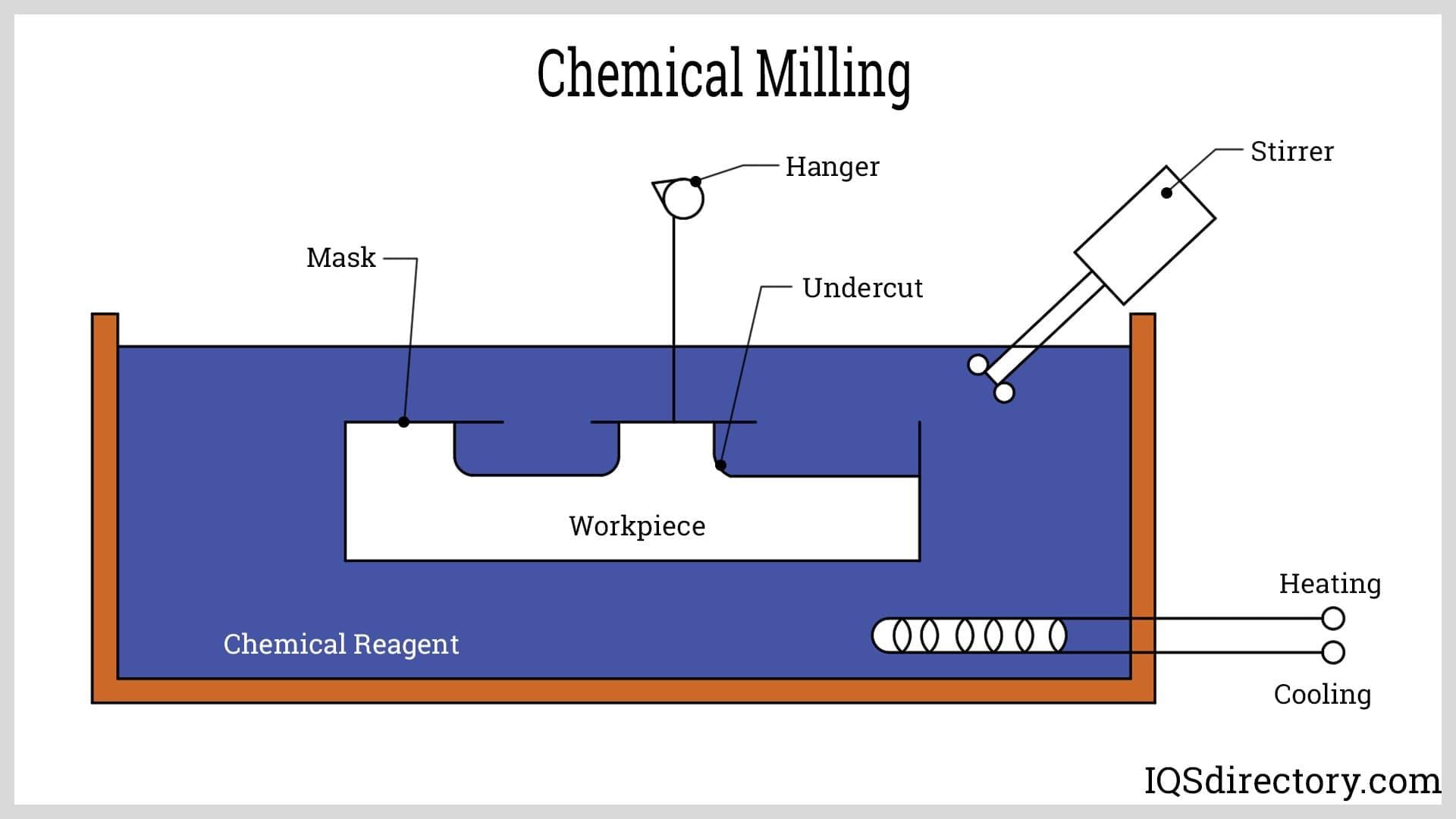
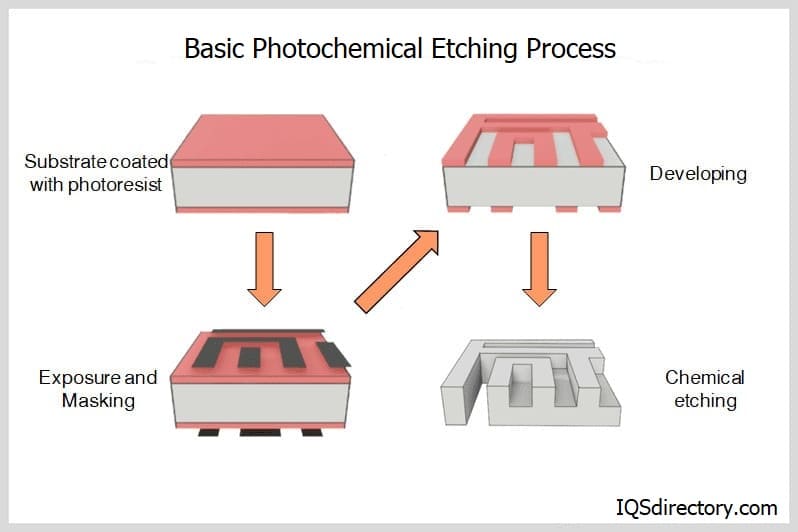
Chemical etchant serves as the foundation for the operation of chemical machining. A mixture of potent acids that react with metal is called an etchant. When submerged, the etchant reacts with the workpiece, dissolving the metal from the workpiece at a consistent rate. Before machining, an elemental coating resistant to the chemical reagent "maskant" is applied to the workpiece to achieve the required shape or structure.
Applying an appropriate mask to all the regions where we don’t want the etchant to react allows us to achieve localized machining, making the machining area visible for the required metal removal. Temperature, agitation, acid concentration, and the desired depth of the cut or etch are just a few variables considered when determining how long to leave the reagent in place. Finally, the chemical is removed from the part and polished once the desired outcome has been obtained.
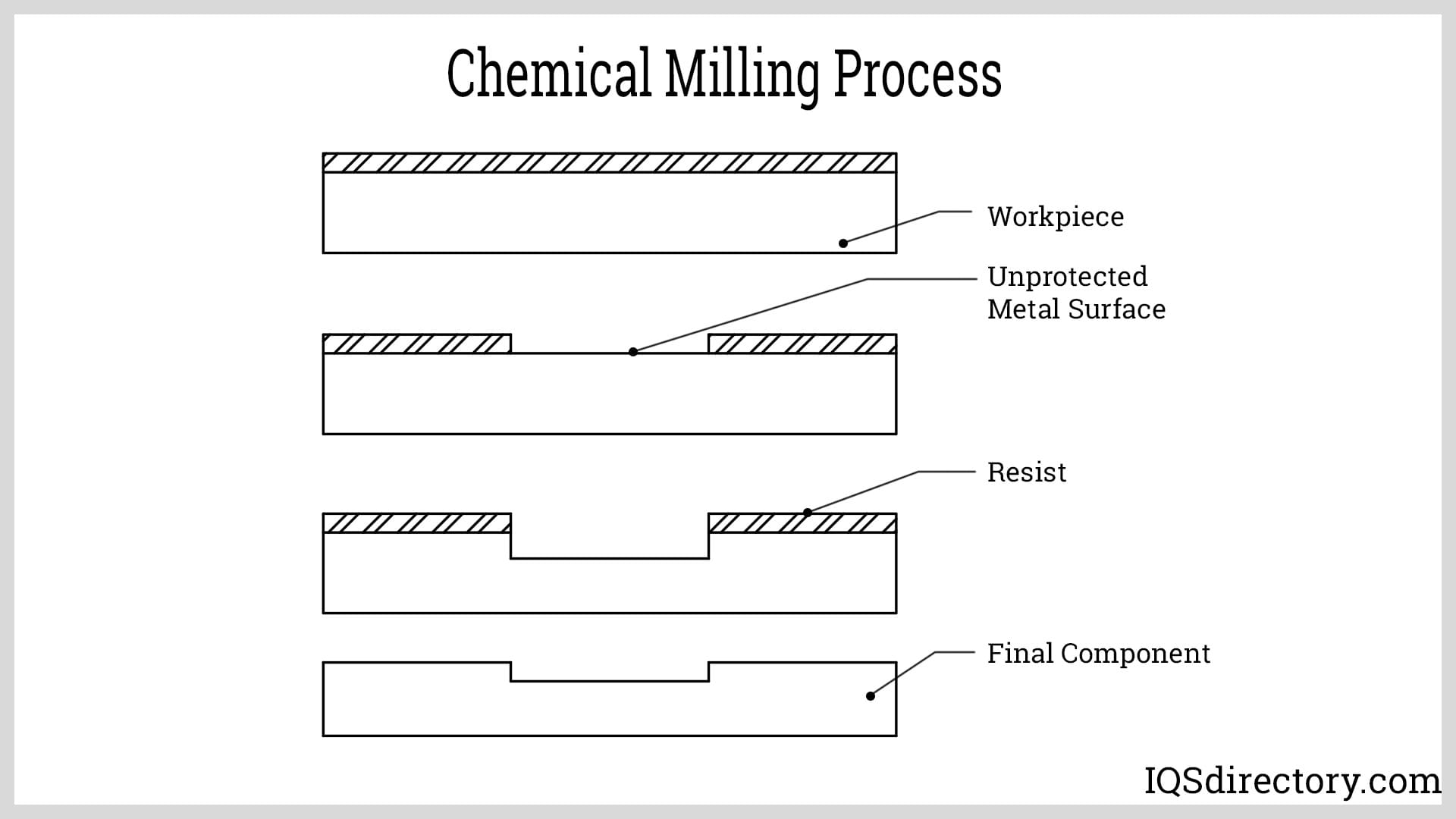
Step-by-Step Process of Chemical Milling
Surface Cleaning: Cleaning is the first step to ensure the workpiece's surface is free of impurities, corrosion, and foreign objects. High-pressure water jets, alcoholic liquids, and diluted HCl are typically used to execute it. Poor cleaning leads to inaccurate final measurements, poor maskant adherence, and poor metal dissolving. In addition, improper cleaning can cause the maskant to peel off, ruining the geometry by allowing the etchant to run behind the mask. The workpiece is dried with hot air blowers after it has been washed. Modern CNC machinery is always used to carry out the cleaning operation.
Masking: It involves coating the workpiece's surface with maskant. First, the workpiece is covered in a coating of polymer or rubber. Then, masking stops the etching process from going on in a region that doesn't need to be machined. Except for the sections that will be machined, the entire workpiece is covered in masking.
Etching: This is the procedure that removes the necessary metal. Next, the workpiece is dipped into the chemical reagent tank with the heater and stirrer turned on after a specific masking job. The etchant reacts with the workpiece's unmasked portions as soon as it is dipped. As a result, the workpiece reacts with the highly concentrated acid, changing its chemical characteristics. The predetermined sections melt due to this reaction, layer by layer, separating from the workpiece. In this procedure, the length of the workpiece's dip coincides exactly with the depth of the cut. Therefore, the more metal is removed from the workpiece, the longer it remains in the etchant. Contrarily, this is also true.
Demasking: Peeling off the maskant after the etching process is known as demasking. After the maskant has been removed, the workpiece is once more transported for cleaning, where any remaining etchant is removed using pressured cold water. The artwork is then dried and prepared for delivery.
Advantages of Chemical Milling
- This machining technique uniformly removes metal.
- excellent surface quality and precise tolerances
- Complex curves may be machined with ease.
- simultaneous removal of material along all axes
- An operator with a lower skill level can be utilized.
- On the workpiece, there is no mechanical stress.
- little upfront cost
- low cost of machining
Disadvantages of Chemical Milling
- less operator safety because even a small amount of etchant on the skin might be harmful
- After milling, there is a chance of rusting.
- Poor surface polish can result from alloy machining.
- The process could be more sustainable.
- Byproduct disposal can damage the environment.
- The material removal rate (MRR) is lower than other machining techniques.
- The potential for bubble development could lead to poor machining.
Applications of Chemical Milling
- Complex contour weight loss is not attainable with traditional techniques.
- machining of delicate, thin parts
- It is used to cut the internal contours of a hole.
- It is utilized by the car and aviation sectors.
- creation of fine meshes and screens
- removing metal from areas where holding a workpiece is challenging
- aerospace parts

Choosing the Proper Chemical Milling Company
To make sure you have the most positive outcome when purchasing Chemical Milling from a Chemical Milling Company, it is important to compare at least 5 or 6 Companies using our Chemical Milling directory. Each Chemical Milling Company has a business profile page that highlights their areas of experience and capabilities and a contact form to directly communicate with the manufacturer for more information or request a quote. Review each Chemical Milling business website using our patented website previewer to get an idea of what each business specializes in, and then use our simple RFQ form to contact multiple Chemical Milling companies with the same quote.







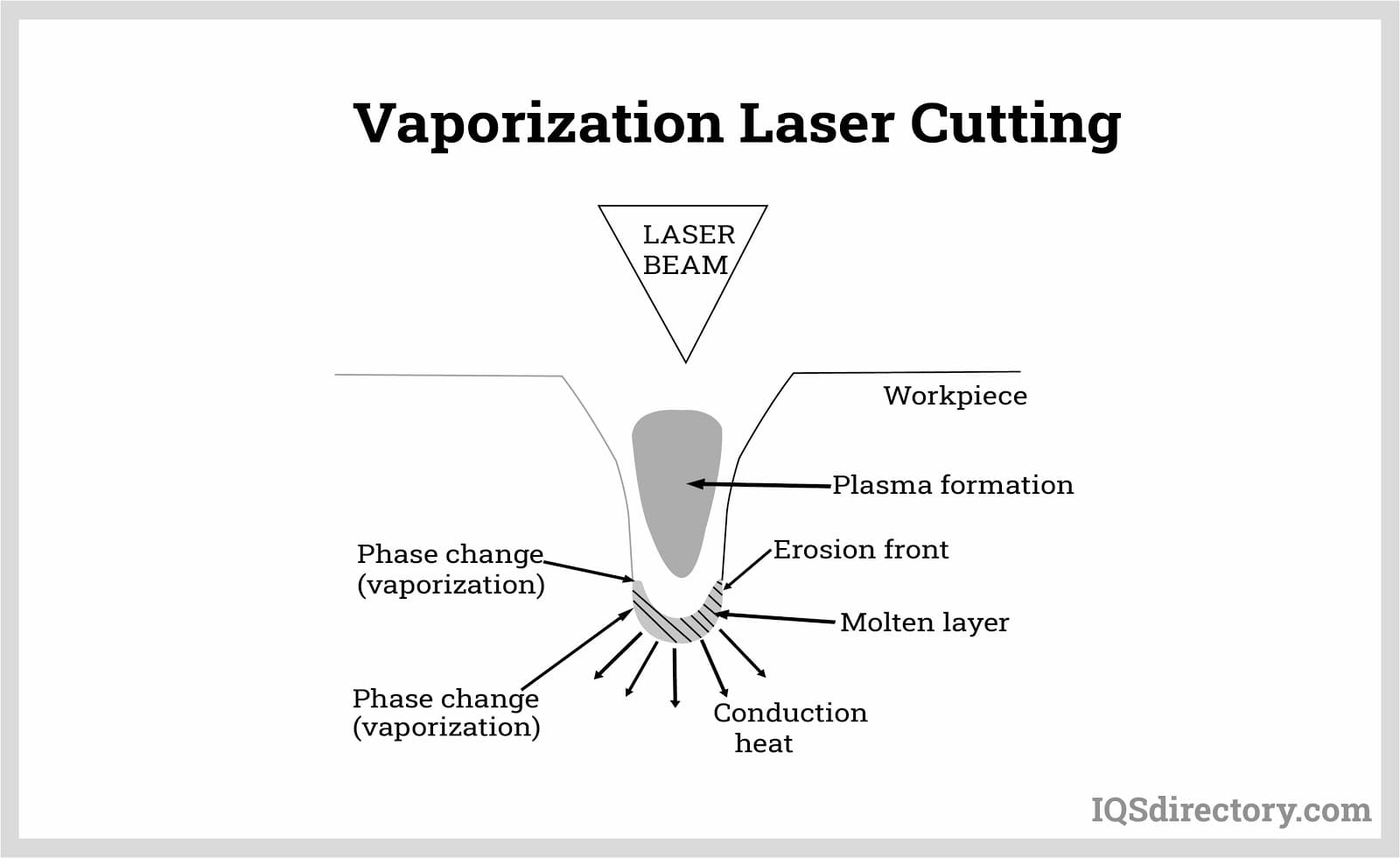
 Broaching
Broaching CNC Machining
CNC Machining Expanded Metals
Expanded Metals Laser Cutting
Laser Cutting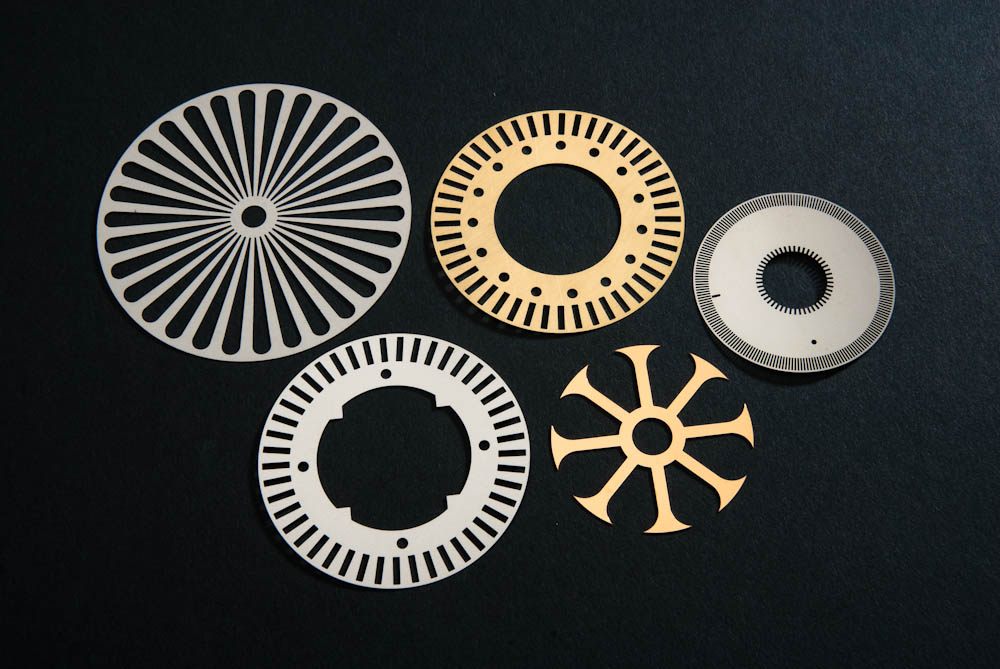 Metal Etching
Metal Etching Metal Fabrication
Metal Fabrication Perforated Metals
Perforated Metals Screw Machine Products
Screw Machine Products Metal Stampings
Metal Stampings Sheet Metal Fabrication
Sheet Metal Fabrication Tube Fabrication
Tube Fabrication Water Jet Cutting
Water Jet Cutting Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services